Systolic blood pressures of severely injured children are very often hypertensive compared with APLS ‘norms’. A lower pulse rate is associated with more severe brain injury

Comparing the systolic blood pressure (SBP) and pulse rate (PR) in injured children with and without traumatic brain injury
Resuscitation. 2010 Apr;81(4):418-21
Category Archives: Resus
Life-saving medicine
Optimum depth of neonatal chest compressions
A retrospective study of infant chest CT scans using mathematical modelling and a number of assumptions suggests that neonatal CPR according to AAP/AHA guidelines of compressing to one third anteroposterior chest wall diameter should provide a superior ejection fraction to 1/4 depth and should generate less risk for over-compression than 1/2 AP compression depth.
Evaluation of the Neonatal Resuscitation Program’s recommended chest compression depth using computerized tomography imaging
Resuscitation. 2010 May;81(5):544-8
Compare their conclusions with those of the authors of this case series of arterial-line monitored cardiac arrests in infants with a median age of one month
Hospital bypass for cardiac arrest?
A Japanese study of over 10,000 patients demonstrated improved neurological outcome in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients who were taken to hospitals designated as ‘critical care medical centres’, where neurologically favorable 1-month survival was greater [6.7% versus 2.8%, P < 0.001] despite a slightly longer call-hospital arrival interval [30.6 min vs 27.2, p < 0.001]. If return of spontaneous circulation was achieved pre-hospital, there was no difference in survival. It is unclear what factors, such as more interventional cardiology or therapeutic hypothermia, made the difference in the critical care centres.
Impact of transport to critical care medical centers on outcomes after
out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
Resuscitation. 2010 May;81(5):549-54
Best position for CPR
A study using volunteer doctors and nurses in simulated cardiac arrest resuscitations compared three different positions for delivering CPR: standing, kneeling by the patient, or standing on a “taboret”. They measured rescuer fatigue and effectiveness of CPR. They conclude that CPR is best performed in a kneeling position in that it maximizes duration of effective chest compression and minimizes back pain. The authors recommend if two or more experienced healthcare providers are available to perform CPR, alternating rescuers every 2 min in the kneeling or standing on a taboret positions, and every 1min in the standing on the floor position in order to minimize rescuer fatigue.
Rescuer fatigue and cardiopulmonary resuscitation positions: A randomized controlled crossover trial
Resuscitation. 2010 May;81(5):579-84
Early CT and post-arrest outcome
A study on the early CT appearances of post-cardiac arrest patients shows two signs to be of importance – loss of boundary (LOB) between white and grey matter (at the level of the basal ganglia), and cortical sulcal effacement (SE). These features were more prevalent in patients who had > 20 minutes of arrest time and were associated with a worse neurological outcome at six months.
Early CT signs in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest survivors: Temporal profile and
prognostic significance
Resuscitation. 2010 May;81(5):534-8
STEMI and PCI guidelines
Lots of interesting and up to date information in this thick document from December 2009
Full text is available here
2009 Focused Updates: ACC/AHA Guidelines for the Management of Patients With ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (Updating the 2004 Guideline and 2007 Focused Update) and ACC/AHA/SCAI Guidelines on Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (Updating the 2005 Guideline and 2007 Focused Update)
Protected: Positive capnography in cadavers
Thoracic Aortic Disease Guidelines
Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Thoracic Aortic Disease have been published by a collaboration between a number of professional bodies including the American Heart Association.
Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Thoracic Aortic Disease
Circulation. 2010 Apr 6;121(13):e266-369 – free Full Text as PDF
HTML full text
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy/Dysplasia
This disease may result in sudden cardiac death in young people, and the assessment of patients who present with dysrhythmias or syncope should prompt a review of the ECG for suggestive features of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy/Dysplasia (as well as ischaemia, conduction deficits, WPW syndrome, Brugada syndrome, and prolonged QT interval).
A Task force has revised its diagnostic criteria for the disease, listed as major and minor criteria pertaining to family history, ECG, echo, MRI, and angiographic features. The ECG features that front line doctors need to be on the look out for include:
- Inverted T waves in right precordial leads (V1, V2, and V3) or beyond in individual >14 years of age (in the absence of complete right bundle-branch block QR>120 ms)
- Inverted T waves in leads V1 and V2 in individual>14 years of age (in the absence of complete right bundle-branch block) or in V4, V5, or V6
- Inverted T waves in leads V1, V2, V3, and V4 in individual>14 years of age in the presence of complete right bundle-branch block
- Epsilon wave (reproducible low-amplitude signals between end of QRS complex to onset of the T wave) in the right precordial leads (V1 to V3)
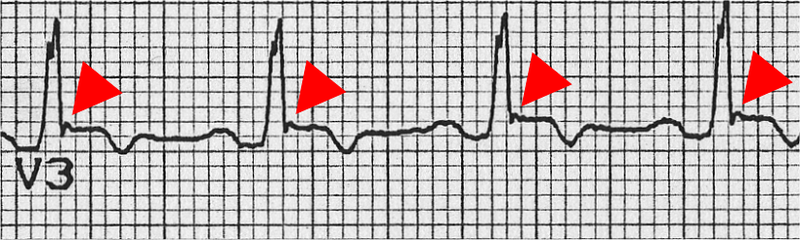
- Nonsustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia of left bundle-branch morphology with superior axis (negative or indeterminate QRS in leads II, III, and aVF and positive in lead aVL)
- Nonsustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia of RV outflow configuration, left bundle-branch block morphology with inferior axis (positive QRS in leads II, III, and aVF and negative in lead aVL) or of unknown axis
- >500 ventricular extrasystoles per 24 hours (Holter)
Diagnosis of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy/Dysplasia Proposed Modification of the Task Force Criteria
Circulation. 2010 Apr 6;121(13):1533-41
More info on this disease from the European Society of Cardiology here
Crystalloids vs colloids and cardiac output
It is said that when using crystalloids, two to four times more fluid may be required to restore and maintain intravascular fluid volume compared with colloids, although true evidence is scarce. The ratio in the SAFE study comparing albumin with saline resuscitation was 1:1.3, however.
A single-centre, single- blinded, randomized clinical trial was carried out on 24 critically ill sepsis and 24 non-sepsis patients with clinical hypovolaemia, assigned to loading with normal saline, gelatin 4%, hydroxyethyl starch 6% or albumin 5% in a 90-min (delta) central venous pressure (CVP)-guided fluid loading protocol. Haemodynamic monitoring using transpulmonary thermodilution was done each 30 min to measure, among other things, global end-diastolic volume and cardiac indices (GEDVI, CI). The reason sepsis was looked at was because of a suggestion in the SAFE study of benefit from albumin in the pre-defined sepsis subgroup.
Independent of underlying disease, CVP and GEDVI increased more after colloid than saline loading (P = 0.018), so that CI increased by about 2% after saline and 12% after colloid loading (P = 0.029).
Their results agree with the traditional (pre-SAFE) idea of ratios of crystalloid:colloid, since the difference in cardiac output increase multiplied by the difference in volume infused was three for colloids versus saline.
Take home message? Even though an outcome benefit has not yet been conclusively demonstrated, colloids such as albumin increase pre-load and cardiac index more effectively than equivalent volumes of crystalloid in hypovolaemic critically ill patients.
Greater cardiac response of colloid than saline fluid loading in septic and non-septic critically ill patients with clinical hypovolaemia
Intensive Care Med. 2010 Apr;36(4):697-701
